Condenser Inspection for Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers Within Industry
Condenser Inspection for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Within Industry is a blog article about the process of condenser inspection. It explains the system's benefits, what goes into the process, and how to get started. If you're looking for information on how to keep your condensers in good shape, this article is a great place to start!
What are the different types of condenser inspection?
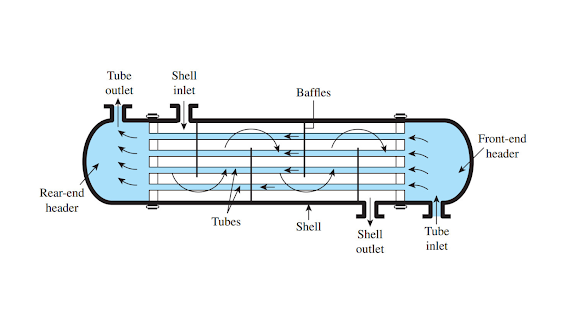
Many different types of condenser inspection can be conducted on heat exchangers within the industry. A typical assessment would consist of a visual examination for signs of corrosion and debris, stack height and vane clearance measurement, gas flow measurements, and thermal analysis. The specific type of inspection will depend on the particular condition of the heat exchanger.
Corrosion is a significant concern on shell and tube heat exchangers due to their exposed metal surfaces. Signs of corrosion can include pitting or oxidation on the metal surface, leading to failure. Debris accumulation can also be a sign of corrosion, as can excessively wear on fan blades or vanes. Measuring stack height and vane clearance can help determine if the heat exchanger is in danger of collapse or damage from excessive debris accumulation. Gas flow measurements can help identify any problems with gas flow, such as blockages or low flows. Thermal analysis can indicate whether the heat transfer rate is within acceptable limits.
Each type of condenser inspection has its guidelines and requirements, which must be followed when conducting the examination. Failure to follow these guidelines may result in inaccurate results or equipment failure.
How is a condenser inspection performed?
A condenser inspection is typically performed on a shell and tube heat exchanger when it is suspected that the exchanger may need replacement. The review will include a visual inspection of all parts of the exchanger and an inspection for cracks or other signs of damage. If any problems are found, the exchanger will be replaced.
How are condenser inspections done inside and outside the fluidized bed?
Condenser inspections are typically conducted inside and outside a fluidized bed reactor to identify potential problems. Checks can be done with an internal or external inspection method. Internal inspection methods include visual observation, using a microscope, X-ray, or ultrasound; external inspection methods include thermal imaging, water flood testing, or gas sampling.
The following are some common problems that may be found during condenser inspections:
1. Frozen condensers: If the condenser is frozen, it may not be able to produce enough heat to keep the reactor running correctly. This could lead to problems such as reduced production and emissions, increased fuel costs, and even plant shutdowns.
2. Defective coils: Coils can become damaged from overheating or other factors and must be replaced. If this is not done promptly, it could cause the condenser to overheat and fail altogether.
3. Failed thermocouples: Thermocouples are virtual devices that help monitor temperature throughout the system. If they fail, it can lead to inaccurate readings and incorrect diagnoses of system issues. This could lead to costly repairs and even plant shutdowns.
What is a "Clean" Condenser Inspection?
A clean condenser inspection is essential in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of your shell and tube heat exchanger.
Shell and tube heat exchangers are often used in industrial settings to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another. This type of equipment can be critical for applications such as Refinery, Chemical Processing, Food Processing, Power Generation, and Aerospace.
A clean condenser inspection ensures that your shell and tube heat exchanger are operating at their best possible capacity. By performing a sanitary condenser inspection, you can identify any issues with the system that may cause degradation or failure.
You typically inspect all system components for damage or wear during a clean condenser inspection. You will also check for any leaks or malfunctions that may be causing undue stress on the system. By identifying these issues early on, you can prevent them from becoming serious problems down the road.
How long does a condenser inspection typically last?
A condenser inspection typically lasts around two hours. The inspector will test the cooling system to ensure that it works correctly and produces adequate cold air. They will also inspect the insulation, metalwork, and fans to ensure they are in good condition.
.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment