Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: A Comprehensive Overview
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a vital component used in numerous industrial processes for efficient heat transfer. In this article, we will delve into the features, working principle, and applications of this popular heat exchanger.
Understanding the Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
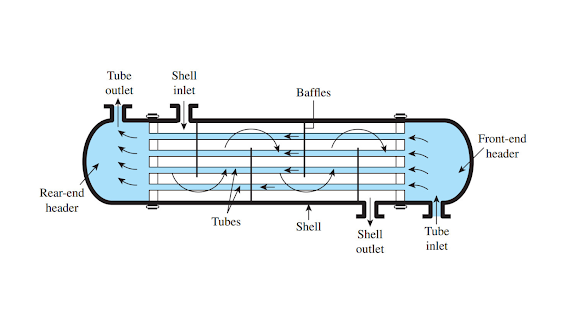
The shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a cylindrical shell that encloses a bundle of tubes. These tubes are responsible for carrying the two fluids involved in the heat exchange process. One fluid flows through the tubes, known as the "tube-side," while the other fluid circulates around the tubes within the shell, referred to as the "shell-side." The fluids never come into direct contact, making this design suitable for a wide range of applications.
Working Principle
The heat exchange process in a shell and tube exchanger follows a straightforward principle. When two fluids at different temperatures come into contact through the tube and shell arrangement, heat transfer occurs. The fluid with higher temperature releases its thermal energy to the fluid with lower temperature, balancing the heat distribution between the two.
The effectiveness of the heat transfer depends on several factors, such as the flow rates of both fluids, the physical properties of the fluids, and the overall design of the exchanger. Engineers can optimize these factors to achieve the desired level of heat transfer efficiency.
Features of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers boast several features that make them highly sought-after in various industries:
1. Versatility
One of the primary advantages of this type of heat exchanger is its versatility. It can handle a wide range of temperature and pressure differentials, making it suitable for both high and low-temperature applications.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency
Shell and tube heat exchangers are renowned for their excellent heat transfer capabilities. The large surface area provided by the numerous tubes facilitates efficient heat exchange between the two fluids, leading to optimal performance.
3. Durability and Reliability
Constructed from robust materials, such as stainless steel, copper, or titanium, shell and tube heat exchangers are highly durable and can withstand harsh operating conditions. Their design and construction ensure long-lasting and reliable performance.
4. Easy Maintenance
Maintaining a shell and tube heat exchanger is relatively straightforward. Regular cleaning and inspection of the tubes help prevent fouling and ensure consistent efficiency.
Applications
The versatility and efficiency of shell and tube heat exchangers make them indispensable in numerous industrial sectors:
1. Petrochemical Industry
Shell and tube exchangers are extensively used in the petrochemical industry for processes such as oil refining, natural gas processing, and chemical production.
2. Power Generation
In power plants, these heat exchangers play a crucial role in condensing steam and cooling turbine generator systems.
3. HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in buildings often employ shell and tube heat exchangers for temperature regulation and energy efficiency.
4. Food and Beverage Industry
In food processing, shell and tube heat exchangers are utilized for pasteurization, sterilization, and cooling applications.
Conclusion
The shell and tube heat exchanger stands as a cornerstone in modern industrial processes, enabling efficient heat transfer between fluids while ensuring reliability and durability. Its versatile design and excellent performance make it a preferred choice for various applications, contributing to enhanced energy efficiency and overall productivity in numerous industries.
.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment